Author: Shumaiza Iqbal
Depression
is the most common mental illness that covered our diverse range of the
population. It negatively affects the mood, thinking patterns and behaviour.
Depression causes the feelings of personal distress, socially dysfunctions and
this all may lead to suicidal ideation and related problems. One of the most
effective treatments of depression is Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT). According to the empirical and research
evidence CBT is effective for the treatment of the depression.
CBT was
developed by Aaron T. Back in the 1960s, and till now it was explained and
studied more extensively. Aaron T. Back explained that negative life events
play a major role in the development of depression and these negative life
events lead towards distorted and negative thinking. In back’s model, he
explained that people with negative cognition have negative beliefs and schemas
that mostly developed from their early childhood experiences. Whenever a
depressed patient passes through the phase of any adverse life events, these
beliefs will be active and leads to negative automatic thoughts (NAT) about
self, world and the future that terms as cognitive tirade in CBT.
In CBT,
Beck helps the patients to change their thought patterns that will improve
their mood and facilities in the coping their stress(Dobson & Dobson,
2009).
In CBT
treatment, therapist collaboratively works with the client that will encourage
the client to work as an active partner in the therapeutic process. Standard
treatment sessions will be 12-15 sessions, and each session remained until
40-45 mints. Each session contained three parts of the session, i.e. initial,
middle and end part. Initial part constitutes with mood check, agenda setting,
obtaining update, review of homework, agenda hierarchy. In the middle part, CBT
techniques will be thought to the clients for their specific problems and
therapist collaboratively assigned the homework while in the final part,
therapist elicited a summary and took feedback from the client.
The
following are the treatment plane that a therapist can opt under the treatment
CBT for depression.
Development of the Therapeutic Relationship
Development
of a positive alliance with the client is significant in the initial session.
Strong trust and rapport will give positive and great outcomes of the treatment.
Good counselling skills with accurate understanding with the therapy,
collaborative decision making, taking feedback, empathy relationship,
alleviating client’s distress all will leads to build a strong report with the
client(Wenzel, Brown & Beck 2008).
Assessment Sessions
Accurate
and proper assessment took an important role in the treatment. It helps in the
correct diagnosis as well as proper case conceptualization of the client,
identification of important problems, goals setting, therapeutic alliance and
also socializes the therapist with the client.
Assessment
should be done both a formal and informal way. Informal assessment
Psychological tests, Questionnaires should be filled from the client whereas
demographics, presenting complaints, history of present illness and
precipitating factors, psychiatric history, family history, developmental
history etc.
Cognitive Case Conceptualization
Case
conceptualization is the backbone of the CBT. It helps the therapist to plane
an efficient and effective treatment plane. CBT is based on the cognitive model
that well explained the client’s emotions, behaviours and physiology influenced
by the perception of events. Case formulation helps the client to understand
how clients believe, emotions linked their behaviour and influenced their
thoughts(Wenzel, Brown & Beck 2008).
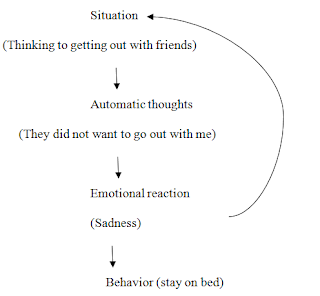
Example of simple case conceptualization is as
Behavioral Activation
Behavioural activation is an important step
towards the improvement and fast recovery of the client. As depressed patients
felt very lethargic and did not want to do any work, it contributed to their
low mood that gave a sense of lack of pleasure and mastery and this situation
leads to negative automatic thoughts (Kuyken, Padesky& Dudley, 2009).
Vicious Cycle of Depressed Client:
Behaviour
activation included two things one is daily activity chart in which clients
have to log out their daily activities and the second thing pleasure and
mastery that predict client’s task completion and how much pleasure they can
get after finishing their work.
Detection of Thoughts and Emotions
Most of
the clients did not able to differentiate between their automatic negative
thoughts (NATs) and emotions. In CBT, therapist’s main work on their thoughts
and behavior because these NATs influenced clients behavior that’s why it’s
important to learn between differentiation between thoughts and emotions so
therapist will able to reconstruct their thoughts(Antony & Barlow, 2010).
First therapist explain the client that what
are their thoughts and emotions then this chart further helpful to the detection
of the thoughts and emotions.
Thought Records
When clients were able to learn about their thoughts and
emotions, then it’s important to tell them what thoughts and emotions are
negative and what is positive. For this purpose, a therapist asks the client to
write down their thought in the form of thought dairy. Thought dairy helped the
therapist to know about their beliefs and thought then therapist have to think
them about all negative thoughts (cognitive distortions and cognitive errors,
i.e. All-or-nothing thinking, jumping to conclusion, Personalization, Selective
abstraction, Magnification or minimization, Overgeneralization etc) because
these basic NATs were influenced their emotions and behaviour (Wenzel, Brown
& Beck 2008).
 Cognitive Reconstructions
Cognitive Reconstructions
Once
when client was able to learn and differentiate about their NATs then clients
are thoughts to ask themselves about the evidences for and against of their
thoughts. It basically is the process of thought reconstructions. When client
evidence about their thoughts then it’s easily to work on it and change or
alternate their thoughts into positive one(Hollon,
Thase& Markowitz, 2002).

Termination and Relapse Prevention
Therapists should begin to prepare their
clients for termination and relapse prevention from initial sessions. In each
goal settings, the therapist should explain to them these techniques will be
thought them for becoming their therapist because their treatment is for short
interval of time and in future after completing their treatment they can use
these techniques by themselves. The initial session will be taken one in a week
but when therapy is going to its end then gradually sessions will be taken as
by weekly and then once a month so that therapist easily and safely terminates
their clients (Boland & Keller, 2002).